Table of Contents
What is thermal imaging?
Thermal imaging is a way of seeing how hot or cold things are using a unique camera. These cameras don’t use regular light like the ones in our phones. Instead, they see heat coming from objects.
Everything that has some heat (which is pretty much everything around us) gives off a kind of light that we can’t see with our eyes.
This light is called infrared. The thermal camera picks up this infrared light and shows it as a picture with different colors.
In these pictures, the colors tell us how hot or cold something is. For example, something very hot might look red or orange, and something cooler might look blue or purple.
People use thermal imaging in many places, especially where machines are used a lot. Thermal imagers are really helpful because they can help find problems before they get too big.
Imagine a machine in a factory getting too hot.
The thermal camera can spot this way before humans would notice it. This keeps everything running smoothly and safely.
Thermal imaging helps people find and solve problems quickly, which saves time and money.
It’s used in many places like factories, buildings, and even by firefighters. This special way of visualizing heat makes things a lot easier and safer in many jobs.
What is a thermal image?
A thermal image is a special kind of picture that shows temperatures. It’s made using a thermal camera, which is different from the cameras we use for regular photos. Instead of capturing what we can see, a thermal camera captures heat from objects in the form of infrared radiation. This radiation is something we can feel as heat, but can’t see with our eyes.
How It’s Different from Regular Photos
Understanding the Colors of Thermal Imagery
In a thermal image, colors don’t show the actual color of things. They show how hot or cold something is. Here’s how it usually works:
What We See in a Thermal Image
What we get is a “temperature map.” This map lets us see the temperature differences in an area. For example:
Who Chooses the Colors in a Thermal Image?
In a thermal image, the colors you see are chosen by the person using the thermal camera. These colors aren’t random; they’re part of what’s called a “color palette.” A color palette is a set of colors that the camera uses to show different temperatures. The person using the camera can pick which palette to use based on what they need to see.
Different Types of Color Palettes and Their Uses
1. Rainbow Palette
- What It Looks Like: A mix of many colors, like a rainbow.
- Best For: Showing a wide range of temperatures.
- Useful In: General inspections where you need to see a lot of temperature differences.
2. Iron Palette
- What It Looks Like: Shades of red, orange, yellow, and black.
- Best For: High-contrast situations.
- Useful In: Industrial settings, for finding hot spots in machinery.
3. Grayscale Palette
- What It Looks Like: Black, white, and shades of gray.
- Best For: Detailed analysis.
- Useful In: Electrical inspections, where precision is key.
4. High Contrast Palette
- What It Looks Like: Very bright colors against very dark ones.
- Best For: Spotting small differences in temperature.
- Useful In: Building inspections to find leaks or insulation issues.
5. Arctic Palette
- What It Looks Like: Cool colors like blues and greens.
- Best For: Identifying cooler areas.
- Useful In: HVAC system inspections.
Why Different Palettes are Useful
Each color palette highlights different aspects of the temperature data. For example:
- Rainbow Palette: Good for quickly spotting temperature differences because it uses many colors.
- Iron Palette: Makes hot areas stand out, useful in mechanical settings.
- Grayscale Palette: Offers fine detail, helping to pinpoint exact areas of concern.
Choosing the Right Palette
Selecting the appropriate color palette in thermal imaging is crucial as it greatly influences the effectiveness of the inspection or analysis. Here are some more detailed examples of different scenarios and the suitable palettes for each:
1. Safety Inspections in Industrial Environments
- Ideal Palette: Iron or Fire Palette.
- Why: These palettes highlight extremely hot areas with bright, vivid colors. This is essential in industrial environments to quickly identify overheating machinery or electrical hotspots, which could pose safety hazards.
2. Energy Audits for Buildings
- Ideal Palette: Blue-Red or High Contrast Palette.
- Why: These palettes are great for showing subtle differences in temperature, crucial for detecting areas of heat loss in buildings. The Blue-Red palette, with its clear distinction between warm and cool areas, helps in identifying poorly insulated spots or air leaks.
3. Wildlife Research and Animal Studies
- Ideal Palette: Rainbow or Arctic Palette.
- Why: The Rainbow palette, with its wide range of colors, is useful for easily distinguishing animals from their surroundings. The Arctic palette, emphasizing cooler colors, can be helpful during night observations.
4. Electrical and Circuit Board Inspections
- Ideal Palette: Grayscale Palette.
- Why: The Grayscale palette, offering fine gradations between black and white, helps in identifying the slightest variations in temperature. This is crucial for pinpointing hotspots or faults in electrical components.
5. Search and Rescue Operations
- Ideal Palette: Fire Palette or Hot Iron Palette.
- Why: These palettes make human figures stand out against cooler backgrounds, which is vital in search and rescue missions, especially in diverse terrains or at night.
6. Medical Diagnostics and Health Monitoring
- Ideal Palette: Ironbow Palette.
- Why: The Ironbow palette is designed to highlight subtle variations in body temperature, useful for medical diagnostics and monitoring, such as detecting inflammation or poor circulation.
7. HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) System Checks
- Ideal Palette: High Contrast or Arctic Palette.
- Why: These palettes emphasize the contrast between cool airflows and warmer surroundings, making it easier to detect inefficiencies or leaks in HVAC systems.
In each of these examples, the chosen palette plays a pivotal role in enhancing the visibility of crucial details, thereby aiding in accurate and effective analysis or decision-making.
How does a thermal camera see heat?
How Does a Thermal Camera See Heat?
Understanding how a thermal camera “sees” heat involves exploring its unique way of capturing images based on temperature differences, rather than light as traditional cameras do. Here’s a breakdown of this process:
1. Detection of Infrared Radiation
- What Happens: Every object emits infrared radiation as a function of its temperature. The warmer an object is, the more infrared radiation it emits.
- Camera’s Role: A thermal camera is equipped with a special sensor that detects this infrared radiation, which is invisible to the human eye.
2. Converting Infrared to Visual Images
- Process: The camera’s sensor translates the infrared radiation into electronic signals.
- Result: These signals are then processed to produce a visual image that represents the varying temperatures of the scene. This image is what we see as a thermal image.
3. Temperature Representation with Colors
- Color Mapping: The electronic signals are mapped to different colors based on their intensity, which corresponds to the temperature of different objects in the view.
- Visual Output: Hotter objects might appear as red, orange, or yellow, while cooler objects could be blue or purple.
4. Real-Time Imaging
- Dynamic Capture: Thermal cameras can capture these images in real-time, allowing for immediate analysis and decision-making.
- Usefulness: This is particularly useful in situations where rapid responses are necessary, such as in firefighting or emergency search and rescue operations.
5. Sensitivity to Temperature Differences
- Fine Details: Modern thermal cameras are sensitive enough to detect minute differences in temperature, even fractions of a degree.
- Importance: This sensitivity is crucial for applications like electrical inspections, where small hotspots could indicate a potential fault.
6. Non-Contact Measurement
- Safety and Accessibility: Since thermal cameras can detect heat from a distance, they can be used to measure temperatures in hazardous or inaccessible areas.
- Applications: This feature is particularly beneficial in industrial settings for inspecting high-voltage equipment or in healthcare for non-invasive diagnostics.
What is the Special Sensor in a Thermal Camera That Captures Heat?
Inside every thermal camera is a very important part called a “sensor.” This sensor is special because it can detect heat from things around it. Let’s break down how this sensor works in a simple way:
The Heat-Detecting Sensor
- What It Does: The sensor in a thermal camera is like a super-sensitive thermometer that can ‘see’ heat.
- How It Sees Heat: Everything around us gives off some heat. This heat is like a special kind of light that our eyes can’t see, but the sensor in the thermal camera can.
Types of Sensors in Thermal Cameras
- There are mainly two types:
- Microbolometer: This is the most common type in many thermal cameras. It works at room temperature and doesn’t need to be cooled down.
- Cooled Infrared Detectors: These are more sensitive and used in more advanced cameras. They can see smaller differences in heat but need to be kept very cold to work properly.
How the Sensor Creates a Thermal Image
- Catching Heat Rays: The sensor catches the heat rays from different things, like people, animals, or machines.
- Turning Heat into Pictures: It then changes these heat rays into electronic signals. These signals are used to make an image that shows how much heat different things are giving off.
Why the Sensor is Important
- Seeing Heat Differences: The sensor is what allows the thermal camera to see tiny differences in heat, which is really useful.
- Safe and Quick: It lets people find hot spots or cool areas safely and quickly, without having to touch or be near them.
So, the sensor in a thermal camera is very important because it turns the heat that everything gives off into a picture we can see, showing us a world of temperatures that our eyes can’t detect on their own.
Different Types of Thermal Cameras
Thermal cameras come in two main types: cooled and uncooled. This difference is all about the special sensors inside them and whether they need to be kept cold or can work at normal temperatures. Let’s dive into what makes these two types of cameras different:
Cooled Thermal Cameras
- Why They’re Cooled: These cameras have sensors that are very sensitive to heat. To work their best, they need to be kept very cold. When these sensors are cold, they can pick up very small differences in heat.
- How They Work: Cooled sensors are usually kept in a container that brings their temperature way down. This makes them super good at detecting tiny changes in heat.
- Best For: Because they are so sensitive, cooled thermal cameras are great for seeing things that are far away or that only give off a little bit of heat. They’re often used by scientists or the military.
Uncooled Thermal Cameras
- Why They’re Uncooled: These cameras have sensors that work fine at normal temperatures. They don’t need extra cooling to do their job.
- How They Work: The sensors in uncooled cameras react to heat in a different way. They change shape or electricity flow when they heat up, which creates the thermal image.
- Best For: Uncooled cameras are more common and less expensive. They are good enough for most uses, like checking buildings for heat loss, finding people or animals in the dark, or seeing where a machine might be overheating.
Key Differences
- Sensitivity: Cooled cameras are more sensitive and can detect smaller temperature differences.
- Cost and Size: Cooled cameras are usually more expensive and bigger. Uncooled cameras are more affordable and portable.
- Use Cases: Uncooled cameras are great for everyday uses, while cooled cameras are better for specialized tasks that need high sensitivity.
So, whether a thermal camera is cooled or uncooled depends on how sensitive its sensor needs to be. Cooled cameras are like high-powered, super-sensitive tools for special jobs, while uncooled cameras are like handy, everyday tools for a broad range of tasks.
Why are thermal cameras so useful?
Thermal cameras are amazing tools that have become super useful in so many different areas. They’re not just one type of camera; they come in all shapes and sizes, each designed for a specific task. From helping soldiers in war to assisting scientists, their uses are vast and varied. Let’s explore how thermal cameras have been integrated into various fields:
1. Thermal Cameras in UAVs (Drones)
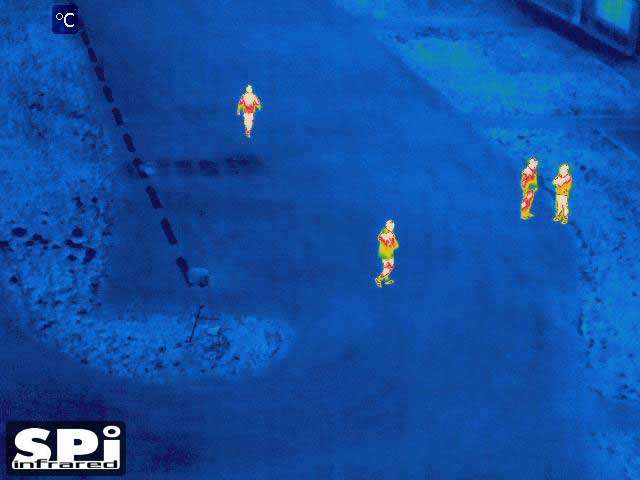

- Use: Drones equipped with thermal cameras are used for things like search and rescue missions, agricultural monitoring, and surveillance.
- Advantage: They can cover large areas from the sky and detect heat signatures that are hard to see from the ground.
2. Streetlight Cameras with Thermal Imaging

- Use: Some streetlights have thermal cameras to help with public safety and traffic monitoring.
- Advantage: They can see things in the dark and help keep roads and communities safe, even at night.
3. Casinos
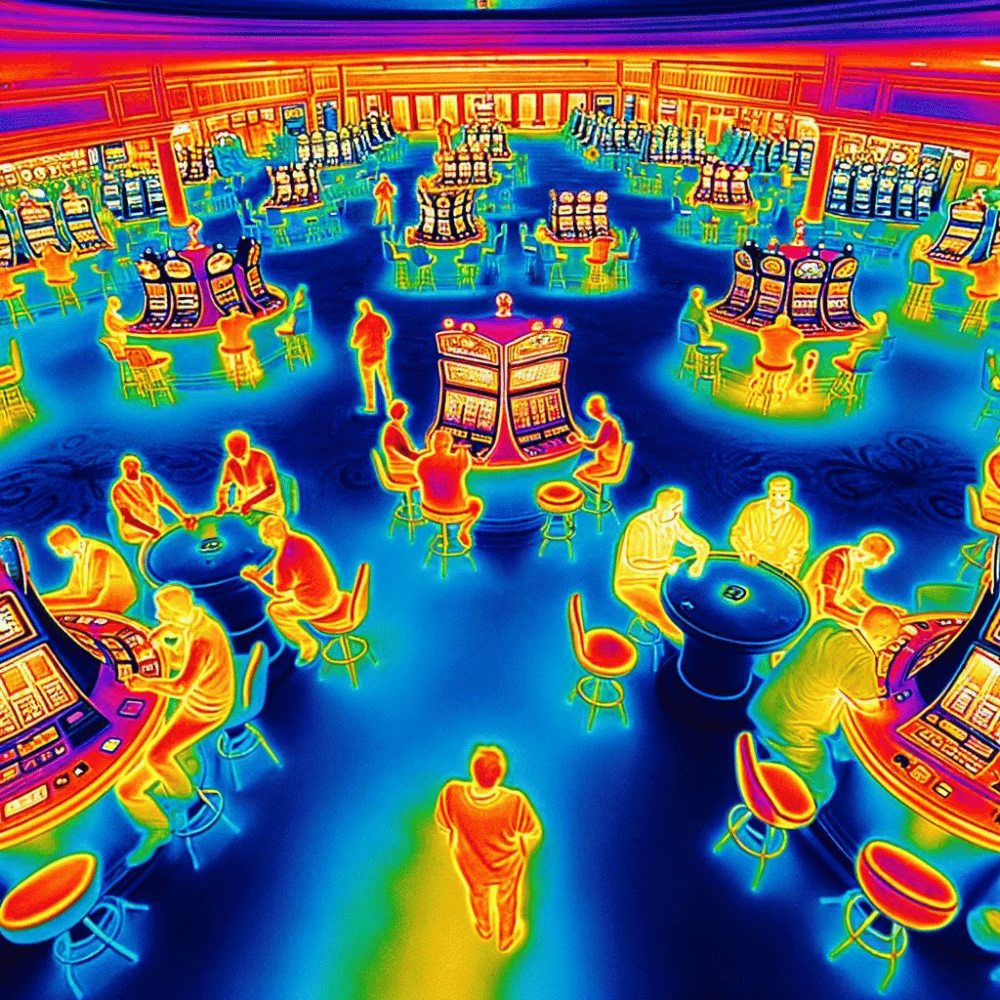
- Use: In casinos, thermal cameras are used for security purposes.
- Advantage: They can detect unusual heat patterns, like someone hiding or electronic devices that shouldn’t be there.
4. Scientific Research
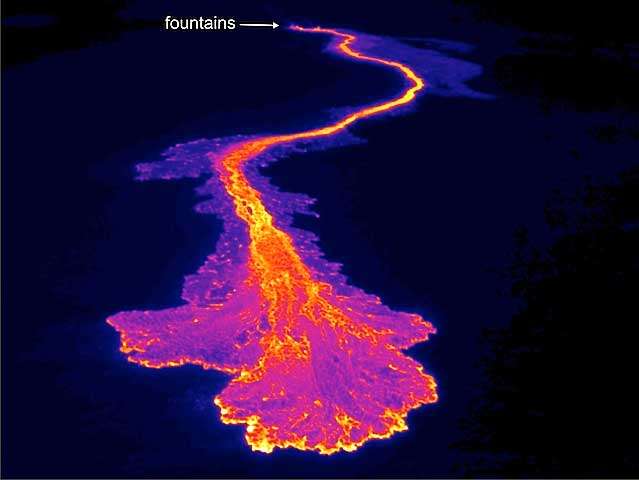

- Use: Scientists use thermal cameras for a variety of studies, from biology to environmental science.
- Advantage: They can study animals without disturbing them or monitor environmental changes.
5. Military Applications

- Use: The military uses thermal cameras for night vision, target identification, and surveillance.
- Advantage: They work in total darkness, giving soldiers a big advantage.
6. Goggles and Monoculars

- Use: Thermal cameras are also used in goggles and monoculars for night vision.
- Advantage: They allow people to see heat signatures in complete darkness, useful for hunting, camping, or security.
7. Self-Driving Autonomous Cars
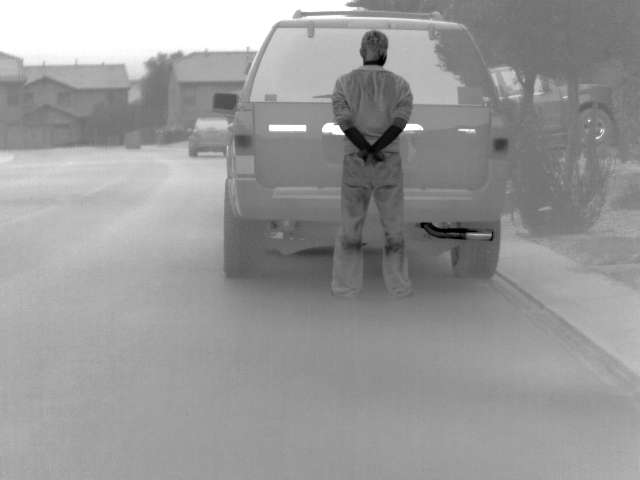

- Use: Some autonomous cars use thermal cameras to detect people, animals, and objects on the road.
- Advantage: They add an extra layer of safety, especially in poor visibility conditions.
8. Astronomy

- Use: Thermal cameras are also used in astronomy to study celestial objects.
- Advantage: They can detect heat from far-away stars and planets, helping astronomers understand the universe better.
9. Airport Security

- Use: Airports use thermal cameras for security checks and monitoring passenger health.
- Advantage: They can quickly scan for signs of fever or detect hidden items based on temperature differences.
10. Sports and Physical Therapy

- Use: Thermal imaging is used in sports to assess muscle performance and in physical therapy to monitor healing.
- Advantage: It provides a non-invasive way to analyze and optimize athletic performance and recovery.
11. Building and Construction
- Use: In construction, thermal cameras help in finding heat leaks, moisture, and structural problems in buildings.
- Advantage: They make it easier to improve energy efficiency and spot potential issues without invasive methods.
Thermal cameras are not just limited to traditional uses like security or industrial inspections. Their ability to ‘see’ heat opens up a world of possibilities, from artistic expression to enhancing safety and efficiency in various industries. These diverse applications showcase the adaptability and value of thermal imaging technology in our everyday lives.
Choosing the Best Thermal Camera or Thermal Imager
Picking the right thermal camera or thermal imager is like choosing the perfect tool for a job. It all depends on what you need to do with it. Here’s a simple guide to help you choose:
1. Resolution
- What It Is: Just like in regular cameras, resolution in thermal cameras is about how clear the picture is.
- Why It Matters: A higher resolution means you can see more details in the thermal image. This is really important if you need to spot very small temperature differences, like in detailed inspections.
2. Sensitivity
- What It Is: Sensitivity is how well the camera can pick up tiny changes in temperature.
- Why It Matters: If you need to see very slight differences (like in scientific research), you should go for a camera that has high sensitivity.
3. Field of View (FOV)
- What It Is: FOV is about how much area the camera can see at one time.
- Why It Matters:
- Wide FOV: Good for scanning big areas quickly (like a large room or outdoor space).
- Narrow FOV: Better for zooming in on something specific (like a small part of a machine).
4. Functionality
- What It Is: This is about the extra features the camera might have.
- Why It Matters: Think about what you’ll use the camera for. Do you need to record videos? Take lots of pictures at once? Share the data with other devices? Make sure the camera can do these things if you need them.
Making Your Choice
- Match Your Needs: Think about what you’ll mostly use the camera for. Is it for checking buildings, working with machines, or maybe for scientific research?
- Consider Your Budget: Higher resolution and sensitivity usually mean a higher price. Decide what’s most important for your needs and how much you can spend.
By keeping these points in mind, you can choose a thermal camera or imager that fits exactly what you need. Whether it’s for checking how well a building is insulated, making sure equipment is running safely, or doing research, the right thermal imaging tool can make a big difference in how well you can do your job.
Take The Thermal Test
You Might Also Want To Read:
Contact UAV1 For Advanced Imaging Solutions
Give Us A Call
If we’re unavailable at the time you call, please leave us a message, and we will get back to you within 24 hours.
+1(702) 369-3966
